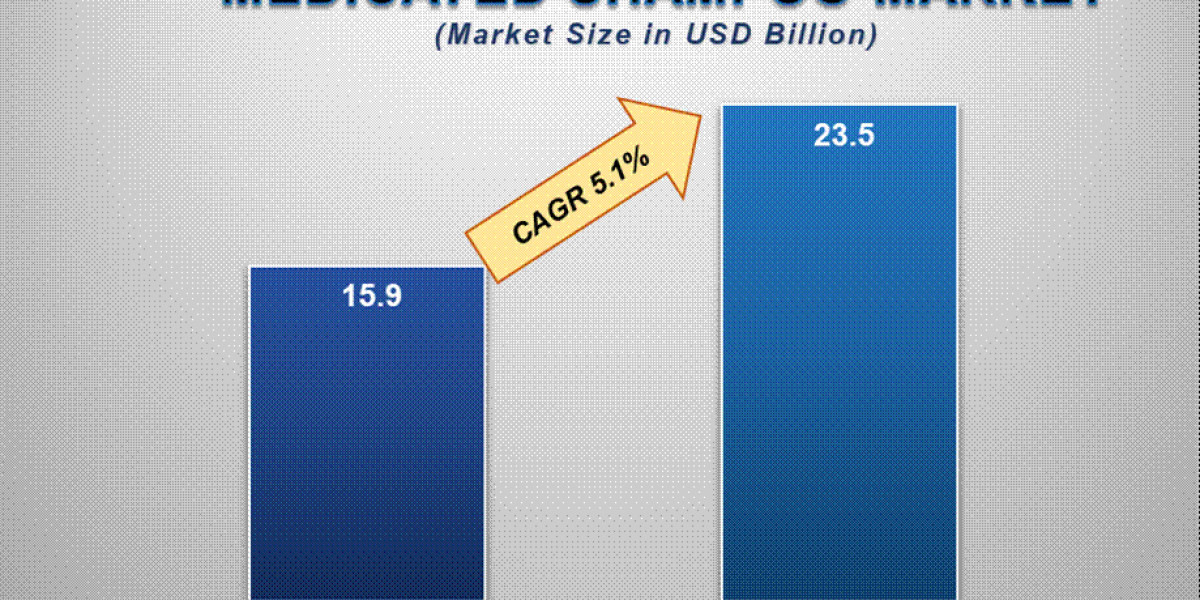
When joints must hold under heat, vibration, and time, a quality-first approach keeps people safe and assets online. Crews face tight schedules, mixed materials, and variable access, so winging it invites leaks or costly do-overs. Our focus here is practical steps that elevate accuracy, document proof, and trim downtime without slowing operations. You’ll see how planning drives repeatable torque, which checks prevent drift, and where sequencing avoids clashes with other trades. We’ll also note real-world examples from plant turnarounds and small retrofit jobs, with simple cues your team can apply tomorrow. The lens is risk and verification; each choice nudges reliability up or down. Treat torque as a process, not a moment. By building controls into setup, tooling, and handoff, you cut failures at their root. In the end, this same discipline supports regulated environments and high-consequence tasks in industrial bolting while keeping time-on-tool efficient.

Scoping the work clearly to set boundaries and avoid blind spots
Start by listing all flanged joints, sizes, gasket types, and access limits, then flag any history of leaks or hot spots. Review the isometric, torque charts, and site constraints, and reference [Hydraulic Torque Wrenches & Bolting Tools] as the pre-job checklist everyone recognizes. Map hold points with operations, EHS, and QA so torque and verification don’t collide with insulation, scaffolding moves, or lift plans. Clear scope equals clear targets; blurry scope breeds rework.

On a light commercial chiller swap, for example, segment the scope by circuit and valve groups to control isolation and testing windows. Define acceptance criteria like final torque values, number of passes, and witness requirements before tools leave the crib. Agree on who signs what, and when. Establish an escalation path for out-of-tolerance studs or damaged nuts so crews don’t stall onsite.

Choosing proper components and inputs for repeatable results
The joint only performs as well as the weakest input, so verify stud grade, lubricant specification, and gasket compatibility with media and temperature. For critical stainless pairs, confirm anti-galling compounds by brand and batch, and share Hydraulic torque wrenches & bolting tools during the kickoff so everyone sees the approved list. Calibrate the hydraulic pump and gauge, and check reaction arms for correct geometry to avoid side loading. Tiny deviations can swing preload far off target.
On a refinery exchanger bundle, swap aged studs showing thread stretch, and lightly chase threads to reduce scatter under load. Use cleanup passes to distribute lubricant evenly, wiping excess from gasket faces to prevent blowouts. Test a single joint to validate torque-lube relationship before full rollout. Bring a backup pump and spare hoses; tiny leaks or valve stickiness can introduce downtime and inconsistency when the schedule is tight.
Sequencing operations and crews to maximize throughput during busy windows
A strong workflow groups flanges by system so isolation and pressure testing align with the plant’s rhythm. Publish a lane-by-lane sequence with pass counts and witness points, and circulate Hydraulic Torque Wrenches & Bolting Tools Usa to keep craft leads aligned across shifts. Assign a dedicated inspector per zone, and match tool sets so each team mirrors torque steps without improvisation. When everyone follows the same beats, performance becomes predictable.
In a turnaround, stage torque tools at the edge of each zone with labeled sockets, hoses, and gauges to cut walk time. Color-code studs once pass one and pass two are complete, then tag final verification with date, time, and operator ID. Five-minute syncs can save five hours of confusion. For small retrofit jobs, sequence joint work around crane picks, avoiding torque passes under suspended loads.
Verifying quality and managing variance with checks that stand up
Quality depends on traceable measurements and controlled steps, not gut feel. Use a torque-angle or snug-pass method to break friction scatter, and include (Hydraulic Torque Wrenches & Bolting Tools) in your verification sheet to standardize evidence. Log tool serials, gauge readings, ambient temperature, and lot numbers for lubricant and gaskets. Data turns opinion into proof.
On a high-pressure steam line, set acceptance bands for residual torque after thermal cycles, and recheck a sample to confirm bolt relaxation within limits. If drift exceeds the band, review lube application, seating sequence, and reaction arm placement before retorquing. Never chase symptoms; fix root causes. Specify Hydraulic Torque Wrenches & Bolting Tools on critical joints where controlled, repeatable preload matters most.
Balancing budget, timelines, and trade-offs without compromising reliability
Money and minutes count, but cutting core controls is a false economy. Build a costed plan that weights labor, tool rental, calibration, and standby spares, and attach (Hydraulic Torque Wrenches & Bolting Tools) so stakeholders see the full picture. Compare time-on-tool for multi-pass versus torque-angle and quantify savings from reduced rework. Pay for control or pay for failure—your choice.
For a small municipal pump station, a modest spend on calibrated gear prevented a week-long slip after a seal failure. Bundle training and procedure refreshers into the schedule to lift crew yield without chasing overtime. Try small, measure impact, then expand with confidence. When constraints bite, prioritize verification at the highest consequence joints, and document the rationale for deferred checks.
Conclusion: A reliability-first mindset ties every step together—from scope clarity and clean inputs to steady sequencing, hard proof, and smart trade-offs. By standardizing what matters, teams deliver safe, repeatable outcomes. Carry these habits from large turnarounds to quick retrofits, and they’ll scale with your workload. In the end, disciplined practices turn pressure into performance, and performance into uptime.