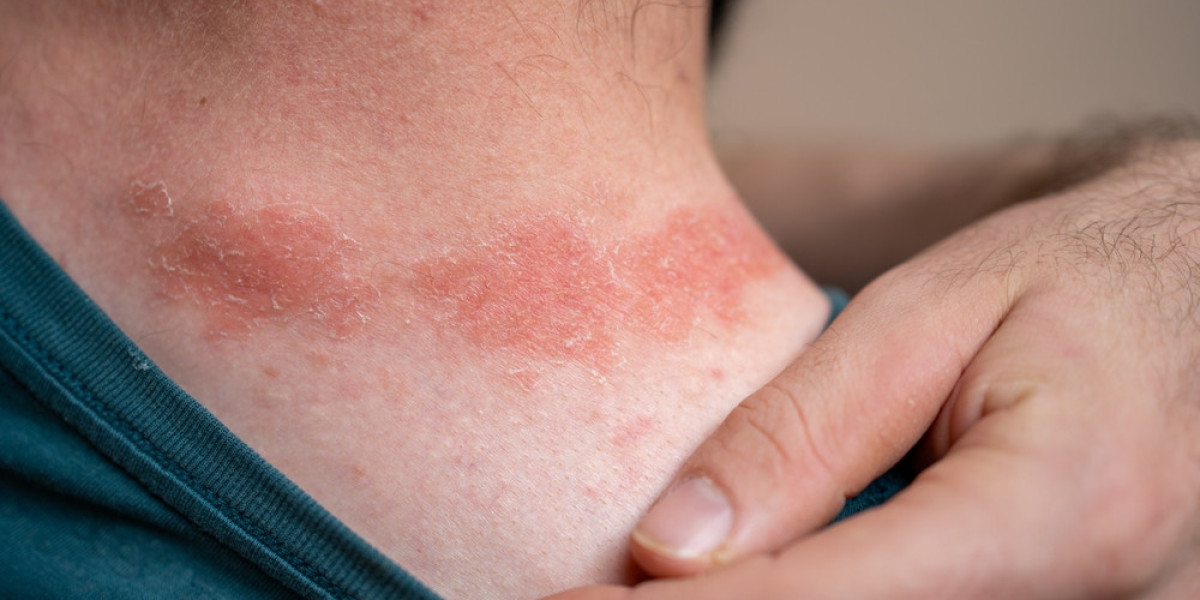
When it comes to chronic skin conditions, few are as well-known, or as confusing, as eczema and psoriasis. But what happens when both appear at the same time? Can a person truly have both psoriasis and eczema? According to this expert overview on psoriasis vs. eczema, while the two conditions are distinct in cause and behavior, people often wonder if psoriasis and eczema exist together.
However, it's rare and often challenging to diagnose. Both diseases involve inflammation and immune system dysregulation, but they affect the skin in different ways. Understanding their overlap is crucial for identifying the most effective treatment approach and enhancing the quality of life for individuals experiencing symptoms of both conditions.
Understanding the Basics
Eczema (Atopic Dermatitis)
Eczema is an inflammatory condition often associated with a weakened skin barrier and an overactive immune response. It causes dry, itchy, and red patches that can ooze or crust. Common triggers include allergens, irritants, temperature changes, and stress.
Psoriasis
Psoriasis, on the other hand, is an autoimmune disease in which the immune system accelerates skin cell turnover, resulting in thick, scaly plaques with a silvery buildup. It's typically chronic and may also be associated with joint inflammation (psoriatic arthritis).
Although both conditions may appear similar, they originate from distinct biological pathways. However, in some individuals, the immune imbalances that drive them can overlap.
Can Eczema and Psoriasis Coexist?
While uncommon, medical studies and dermatologists confirm that people can experience both eczema and psoriasis simultaneously—a condition sometimes referred to as "eczora" or overlap dermatitis.
This coexistence is more than just a visual mix of symptoms; it represents two different inflammatory pathways acting in the same skin. Eczema tends to involve Th2 immune responses, while psoriasis is driven by Th1 and Th17 cells. In certain cases, both pathways are active, resulting in mixed lesions.
Signs That Both May Be Present:
- Scaly, well-defined plaques (typical of psoriasis) appearing alongside itchy, red, oozing patches (typical of eczema)
- Areas where eczema treatments provide partial relief, but psoriasis-like scaling remains
- Symptoms worsening despite standard single-condition treatments
- Lesions on both traditional eczema sites (elbows, neck, behind knees) and psoriasis-prone areas (scalp, lower back)
Because these two diseases require very different therapies, a correct diagnosis is critical.
The Diagnostic Challenge
Even skilled dermatologists can struggle to differentiate between the two when they overlap. A skin biopsy is often the most reliable method to confirm the presence of both conditions.
Misdiagnosis risks include:
- Using the wrong medications (for example, steroid overuse or inappropriate biologics)
- Prolonged flare-ups or treatment resistance
- Increased risk of infection from damaged skin barriers
Expert evaluation, supported by lab testing and clinical history, helps ensure that both conditions are addressed without aggravating the other.
Managing Coexisting Eczema and Psoriasis
When eczema and psoriasis co-occur, treatment must be carefully tailored to manage inflammation without exacerbating dryness or irritation.
Management Tips:
- Follow a dermatologist's care plan: Combination therapy is often required.
- Moisturize regularly: A strong skin barrier reduces eczema flares and limits psoriasis triggers.
- Avoid harsh products: Fragrance-free cleansers and gentle skincare are essential.
- Manage stress: Stress is a major trigger for both conditions.
- Use prescribed medications carefully, including topical steroids, calcineurin inhibitors, and systemic treatments tailored for both types of inflammation.
In some cases, advanced biologic drugs that target multiple immune pathways may provide relief for patients experiencing both disorders.
Conclusion: Research Is Shedding New Light
While having eczema and psoriasis together is rare, ongoing research continues to uncover how these immune-driven conditions overlap—and how to treat them more effectively. If you or someone you know experiences symptoms of both, expert diagnosis and participation in clinical studies can make a real difference.
Learn more about current atopic dermatitis studies exploring new treatments for eczema and related inflammatory skin conditions. These studies are helping to advance the understanding of how immune imbalances contribute to chronic skin diseases and may one day offer better relief for those living with both eczema and psoriasis. Understanding your skin's story is the first step toward lasting comfort and confidence.