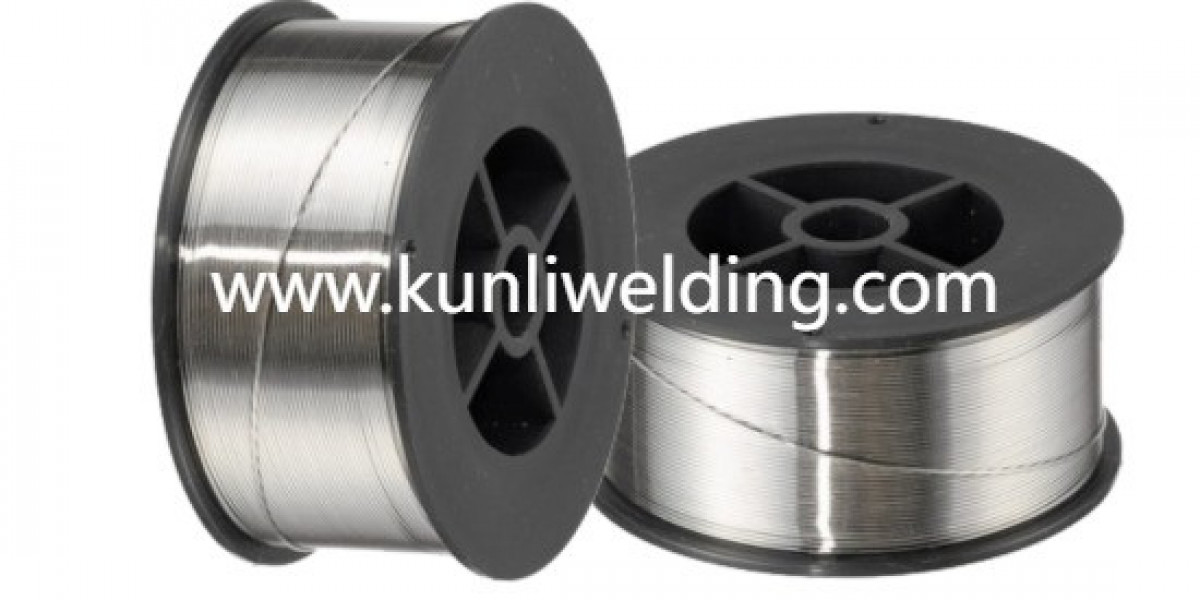
Electrical connections face constant challenges from environmental factors that threaten long term reliability and performance. Terminating braided conductors requires particular attention to techniques that preserve conductivity while protecting against degradation. Kunli Aluminum Braided Wire demands careful handling during connection processes, and Aluminum Braided Wire Manufacturers continue refining recommendations for installation practices. Corrosion prevention stands as a primary concern because aluminum's natural reactivity can compromise connections when moisture and dissimilar metals interact, creating conditions that increase resistance and generate heat over time.
Surface preparation forms the foundation of reliable terminations. Before applying any connector or terminal, installers must remove oxide layers that form naturally on aluminum surfaces. These oxide films act as insulators, preventing intimate metal to metal contact necessary for low resistance connections. Wire brushing with tools specifically designed for aluminum removes oxidation without embedding contaminants that could accelerate future corrosion. Some preparation protocols incorporate chemical treatments that clean surfaces and temporarily inhibit new oxide formation during the connection process.
Compression fittings provide mechanical methods for creating gas tight seals around braided conductors. These connectors work by deforming malleable metal around the wire bundle, forcing individual strands into close contact while excluding air and moisture from the connection zone. Proper compression requires calibrated tools that apply consistent force, ensuring adequate deformation without over compressing and damaging conductor strands. Under compression leaves gaps where moisture can penetrate, while excessive force can break strands and reduce the effective conductor cross section.
Crimp connectors designed specifically for aluminum applications incorporate features that address the metal's unique properties. Internal serrations penetrate surface oxides during crimping, establishing metal to metal contact even if preparation was incomplete. Some designs include inspection windows that allow visual verification of proper strand insertion before crimping. The crimp barrel geometry distributes compression forces evenly across the braided bundle, preventing stress concentrations that might fracture individual strands during installation or subsequent service.
Barrier compounds applied during termination exclude oxygen and moisture from connection interfaces. These materials typically consist of conductive greases or pastes formulated to remain stable across temperature ranges encountered in electrical applications. The compounds fill microscopic voids between conductor strands and connector surfaces, preventing corrosion initiation points from developing. Proper application requires complete coverage without excessive buildup that might interfere with connector seating or create messy installations.
Bimetallic connections present particular challenges when aluminum conductors must interface with copper bus bars or terminals. Direct contact between these metals creates galvanic cells in the presence of moisture, with aluminum corroding preferentially as the more active metal. Specialized transition fittings incorporate barrier materials or coatings that prevent direct aluminum to copper contact while maintaining electrical continuity. Some designs use tin plated surfaces that are compatible with both metals, reducing galvanic potential without introducing high resistance interfaces.
Mechanical fasteners like bolts and clamps can create reliable connections when applied according to specifications that account for aluminum's tendency to creep under sustained pressure. Unlike copper, aluminum continues deforming slowly when subjected to constant compression, potentially loosening connections over time. Belleville washers or spring loaded hardware maintains contact pressure as the conductor relaxes, compensating for creep without requiring periodic retightening. Torque specifications for aluminum terminations typically differ from those used with other conductor materials, requiring attention to installation guidelines.
Ultrasonic welding offers alternative joining methods that create molecular bonds between aluminum surfaces without introducing heat that might alter conductor properties. High frequency vibrations break up surface oxides while bringing metal atoms into close proximity, allowing diffusion bonding to occur at temperatures well below aluminum's melting point. This process works particularly well with braided conductors because individual strands can consolidate into unified termination points that subsequent connectors can grip securely.
Environmental sealing protects completed terminations from exposure conditions that accelerate corrosion. Heat shrink tubing with adhesive liners creates weatherproof barriers around connection points, excluding moisture while providing strain relief that prevents mechanical stress from concentrating at the conductor to connector interface. Some applications require rigid enclosures that completely isolate connections from surrounding environments, particularly in marine or industrial settings where salt spray or chemical exposure creates aggressive corrosion conditions.
Inspection procedures verify connection quality before energizing electrical systems. Resistance measurements across terminations identify high resistance joints that might indicate incomplete compression, inadequate surface preparation, or contamination. Thermographic surveys during initial operation detect hot spots that signal developing problems before they progress to failures. Establishing baseline measurements during commissioning provides reference points for comparison during subsequent maintenance inspections.
Periodic maintenance protocols extend connection service life by addressing degradation before it affects system performance. Visual inspections identify signs of corrosion like white powder deposits or discoloration around termination points. Retorquing mechanical connections compensates for aluminum creep that occurs naturally over time. Some maintenance programs include reapplication of barrier compounds to connections that show evidence of moisture penetration or protective material degradation.
Training programs for installation personnel emphasize proper techniques that prevent common errors leading to premature connection failures. Understanding why specific procedures matter helps installers recognize when field conditions require adaptation while maintaining the protective principles underlying standard practices. Hands on practice with representative materials and connectors builds proficiency that translates to consistent quality across production installations.
Quality control during manufacturing ensures that braided conductors arrive at job sites in condition suitable for reliable termination. Aluminum Braided Wire Manufacturers implement processes that minimize surface contamination and oxidation during production and storage. Packaging designed to exclude moisture preserves conductor surfaces until installation, reducing preparation requirements in the field.
For projects demanding durable electrical connections that maintain integrity throughout service lifespans, understanding termination methods appropriate to aluminum braided conductors supports informed decision making during planning phases. Detailed technical resources and product specifications are available at https://www.kunliwelding.com/product/ for teams developing electrical systems where connection reliability directly impacts safety and operational continuity.