Power cables might seem like simple components, but choosing the wrong type can lead to equipment failure, safety hazards, or compliance issues. Two of the most common power connectors in IT environments are the C13 and C15 types. While they look similar at first glance, the IEC C15 connector offers distinct advantages in specific situations. Understanding when to choose a C15 over a C13 can protect your equipment and ensure optimal performance.
Understanding the Basics: C13 vs C15 Connectors
Before diving into when you should choose one over the other, you need to understand what makes these connectors different. Both the C13 and C15 are IEC (International Electrotechnical Commission) standardized power connectors commonly used in data centers, offices, and networking environments.
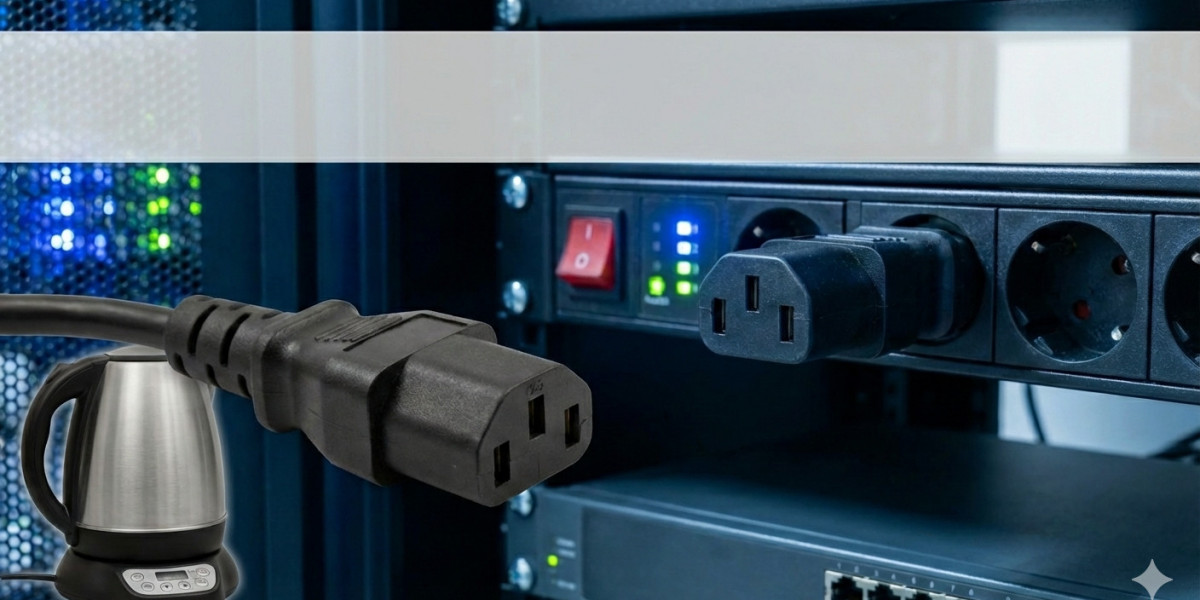
The C13 connector represents the standard power cable inlet you'll find on most computer equipment, monitors, and servers. It handles standard voltage requirements and operates effectively in typical office environments. You've likely plugged and unplugged dozens of C13 cables throughout your career without giving them much thought.
The IEC C15 connector, however, features a notched design that prevents accidental connection with standard C14 inlets. This physical difference exists for an important reason: the C15 connector handles higher temperatures than its C13 counterpart. The notch serves as a safety mechanism, ensuring that equipment designed for higher heat tolerance receives the appropriate power cable.
Temperature Tolerance: The Key Difference
The primary distinction between these two connectors lies in their temperature ratings. A standard C13 connector operates safely at temperatures up to 70°C (158°F). This rating suits most general-purpose IT equipment that doesn't generate excessive heat during operation.
The IEC C15 connector, by contrast, handles temperatures up to 120°C (248°F). This significant increase in heat tolerance makes the C15 essential for specific types of equipment that generate substantial heat during normal operation. The higher temperature rating doesn't just protect the cable itself; it prevents potential fire hazards and ensures consistent power delivery even when equipment runs hot.
When Equipment Demands a C15 Connection
Several categories of equipment specifically require C15 power connections due to their heat generation characteristics. High-performance networking switches often specify C15 connectors because these devices can run continuously at elevated temperatures. The switching components and dense circuitry generate considerable heat, especially in switches handling heavy network traffic.
Electric kettle servers and hot-swap power supplies also demand C15 connections. These components operate in confined spaces with limited airflow, causing ambient temperatures to rise significantly. Using a C13 cable in these situations creates a genuine safety risk, as the lower-rated cable could degrade, melt, or fail entirely under sustained heat exposure.
Power distribution units (PDUs) in data centers frequently incorporate C15 outlets for high-heat equipment. When you rack servers and networking gear that generate substantial thermal output, you need to ensure every component in the power delivery chain can handle those temperatures. A single weak link—like using a C13 cable where a C15 belongs—can compromise your entire setup.
Compatibility Considerations
One practical advantage of the IEC C15 connector relates to backward compatibility. You can plug a C15 connector into both C14 and C16 inlets. This versatility means that if you stock C15 cables, you can use them across a wider range of equipment without worrying about compatibility issues.
However, the reverse doesn't hold true. The notched design of the C16 inlet prevents C13 connectors from fitting, ensuring that only appropriately rated cables connect to high-temperature equipment. This design choice protects both the equipment and users from potentially dangerous mismatches between cable ratings and equipment requirements.
When you manage diverse IT environments, this compatibility factor becomes increasingly important. Rather than maintaining separate inventories of C13 and C15 cables, some facilities standardize on C15 cables for all applications. While this approach costs slightly more upfront, it simplifies inventory management and eliminates the risk of using an under-rated cable.
Data Center Applications
Data centers present unique challenges that often necessitate C15 connections. The dense equipment racks, limited ventilation, and continuous operation create environments where temperatures regularly exceed standard office conditions. Network core switches, blade servers, and high-density storage arrays all generate heat that can overwhelm standard C13 cables.
When you design or upgrade data center infrastructure, you should evaluate each piece of equipment for its thermal output and power requirements. Equipment specification sheets typically indicate whether C15 or C13 connections are required. Following these specifications isn't optional—it's essential for maintaining safe, reliable operations.
Cost and Availability Factors
C15 cables typically cost 10-30% more than equivalent C13 cables due to their enhanced heat tolerance and specialized construction. For large deployments, this price difference adds up quickly. However, the additional cost pales in comparison to the potential expenses associated with equipment failure, downtime, or safety incidents caused by using inappropriate cables.
Availability can also influence your decision. C13 cables enjoy widespread availability through numerous suppliers and retail channels. C15 cables, while readily available from professional IT suppliers, may not stock in typical office supply stores. Planning ahead and maintaining adequate inventory of C15 cables prevents last-minute scrambles when you install or replace high-temperature equipment.
Safety and Compliance Requirements
Many jurisdictions and industry standards mandate specific power cable types for certain applications. Using a C13 cable where specifications require a C15 constitutes a compliance violation that can void warranties, fail safety inspections, or create liability issues. Insurance companies may deny claims related to equipment failure or fire if investigations reveal improper cable usage.
Professional IT environments should maintain documentation showing which equipment requires C15 connections and ensure staff understands the importance of using correct cables. Simple labeling systems can prevent well-intentioned technicians from grabbing the wrong cable during maintenance or installation work.
Making the Right Choice
Choosing between C13 and C15 cables ultimately depends on your specific equipment and operating environment. Always consult equipment documentation and follow manufacturer specifications. When specifications call for a C15 connector, never substitute a C13 as a cost-saving measure or convenience.
For new installations, consider the total cost of ownership rather than just initial cable costs. The IEC C15 connector provides peace of mind, enhanced safety margins, and broader compatibility that justify its modest price premium in many situations. Your equipment, data, and personnel deserve the protection that properly rated power cables provide.