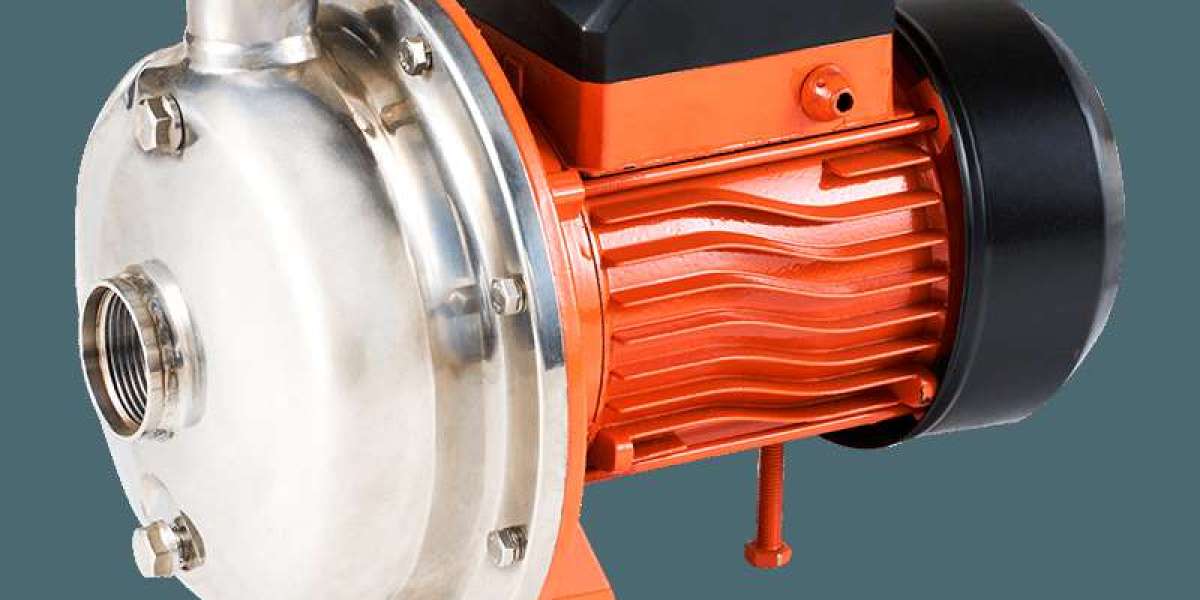
A multistage centrifugal pump is a type of dynamic pump designed to generate high output pressure by employing multiple impellers arranged in series within a single casing. Each impeller-diffuser pair constitutes a "stage," and the fluid gains additional pressure energy as it passes sequentially from one stage to the next. This design principle allows the pump to achieve a much greater total discharge head than a single-stage centrifugal pump of comparable impeller diameter, making it suitable for applications where lifting fluid to great heights or overcoming high system back-pressure is required.
The internal arrangement is key to its function. Fluid enters the pump at the suction inlet and is directed to the first impeller. After being energized, it passes through a diffuser or return channel that converts kinetic energy into pressure and guides the fluid to the inlet of the next impeller. This process repeats in each subsequent stage. The shafts of all impellers are mounted on a common rotor, which is supported by bearings and sealed to prevent leakage. Casing designs can be radially split for easier maintenance or barrel-type for very high-pressure services. The number of stages is determined by the required total head, with each stage contributing a portion of the final pressure.
Proper selection and operation are critical. The pump must be chosen based on required flow rate, total dynamic head, fluid properties, and net positive suction head (NPSH) availability. Operation outside its designed range can cause vibration, recirculation, and premature wear. The operational efficiency and reliability of a multistage centrifugal pump make it a preferred choice for demanding services such as boiler feedwater supply, high-rise building water pressure boosting, reverse osmosis systems, and industrial process water circulation.