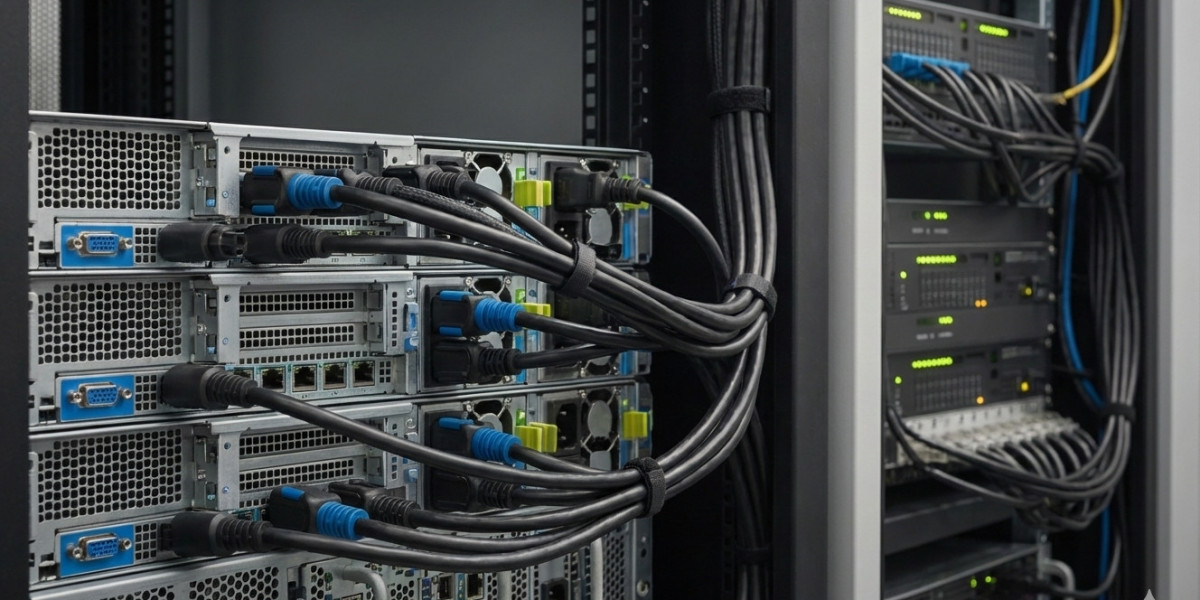
When setting up data centers, server rooms, or high-performance computing environments, choosing the right power cable matters more than most people realize. The IEC C13 cable has served as the industry standard for decades, but its higher-rated cousin, the C15 connector, offers distinct advantages in specific scenarios. Understanding when to upgrade from C13 to C15 can protect your equipment and improve operational efficiency.
Understanding the Basics
What Is an IEC C13 Cable?
The IEC C13 cable represents one of the most common power connectors in the technology world. You'll find this three-pronged connector on most desktop computers, monitors, servers, and networking equipment. The C13 connector plugs into a C14 inlet on your device, creating a secure power connection that handles standard electrical loads.
These cables typically support up to 10 or 15 amps at 250 volts, depending on regional standards. The IEC C13 cable has earned its ubiquity through reliability, cost-effectiveness, and widespread compatibility across countless devices.
What Makes C15 Different?
The C15 connector looks similar to the C13 at first glance, but engineers designed it with a critical difference: a notched shape that prevents accidental connection with standard C14 inlets. This keying mechanism exists for an important reason—the C15 connector handles higher temperatures.
While an IEC C13 cable operates safely up to 70°C (158°F), the C15 connector extends this range to 120°C (248°F). This temperature rating makes C15 connectors essential for equipment that generates significant heat during operation.
Key Differences Between C13 and C15
Temperature Tolerance
The most significant distinction between these connectors lies in their temperature specifications. High-performance servers, enterprise-grade networking equipment, and industrial computing systems often generate substantial heat. When ambient temperatures rise or equipment runs intensive workloads, standard C13 cables can approach their thermal limits.
The C15's higher temperature rating provides a safety margin that prevents connector degradation, reduces fire risk, and extends cable lifespan in demanding environments.
Physical Design
The C15 connector features a distinctive notch on one side that makes it physically incompatible with C14 inlets. Manufacturers implemented this design intentionally—it prevents users from connecting temperature-sensitive equipment with cables that lack adequate thermal protection.
However, C15 inlets (C16) accept both C15 and C13 plugs, offering backward compatibility. This design philosophy ensures you can always use a higher-rated cable with lower-temperature equipment, but never the reverse.
Cost Considerations
IEC C13 cables typically cost less than their C15 counterparts. The price difference reflects the enhanced materials and manufacturing processes required to achieve higher temperature ratings. For large-scale deployments, this cost differential can become significant.
When Should You Upgrade to C15?
High-Density Server Environments
Modern data centers pack servers into increasingly compact spaces. This density creates heat concentrations that push cooling systems to their limits. When servers operate in hot-aisle/cold-aisle configurations or when ambient temperatures regularly exceed 25°C (77°F), upgrading to C15 cables adds an important safety layer.
Network administrators running high-performance computing clusters, blade server systems, or GPU-intensive workloads should seriously consider C15 cables for their superior thermal handling.
Industrial Applications
Manufacturing facilities, warehouses, and industrial settings often expose computing equipment to elevated temperatures. Production lines, heavy machinery, and inadequate climate control can create environments where standard IEC C13 cables operate near their thermal limits.
Industrial computers, programmable logic controllers (PLCs), and automation equipment in these settings benefit from the enhanced temperature tolerance that C15 connectors provide.
Equipment Manufacturer Recommendations
Some equipment manufacturers specify C15 power cables in their documentation. High-end servers, enterprise storage arrays, and specialized networking equipment may require C15 connections to maintain warranty coverage and ensure safe operation.
Always check your equipment specifications before deployment. Using an IEC C13 cable when manufacturers recommend C15 can void warranties and create safety hazards.
Future-Proofing Your Infrastructure
Technology infrastructure represents a significant investment. As equipment generations advance, processing power increases, and power consumption rises, thermal management becomes increasingly critical. Deploying C15 cables during initial installation future-proofs your infrastructure against equipment upgrades that may have higher thermal requirements.
When C13 Remains Sufficient
Standard Office Equipment
Desktop computers, monitors, printers, and typical office networking equipment generate manageable heat levels. These devices operate comfortably within the thermal limits of standard IEC C13 cables. The additional cost of C15 cables provides no practical benefit in these applications.
Climate-Controlled Environments
Well-designed data centers with robust cooling systems maintain ambient temperatures well below the thermal limits of C13 cables. When environmental controls reliably keep temperatures in the 18-27°C (64-80°F) range, and equipment specifications don't require C15 cables, standard IEC C13 cables perform perfectly.
Budget-Constrained Deployments
Small businesses, home offices, and budget-limited projects may not justify the additional expense of C15 cables when equipment doesn't generate excessive heat. Properly specified C13 cables serve these applications reliably and economically.
Making the Right Choice
Evaluate your specific situation using these criteria:
Assess your environment: Measure actual operating temperatures around your equipment. Consider peak temperatures during summer months or heavy processing loads.
Review equipment specifications: Consult manufacturer documentation for power cable requirements. Don't assume—verify the recommended connector type.
Calculate your risk tolerance: Consider the cost of equipment failure, downtime, and potential safety hazards against the incremental cost of C15 cables.
Plan for growth: Consider how your infrastructure might evolve. Equipment upgrades often increase power consumption and heat generation.
Conclusion
The decision to upgrade from an IEC C13 cable to C15 connectors depends on your specific operating environment, equipment requirements, and safety considerations. While C13 cables serve most standard applications effectively, C15 connectors provide essential thermal protection for high-performance equipment and challenging environments.
Don't view C15 cables merely as premium options—treat them as necessary safety equipment when your situation demands enhanced temperature handling. The modest additional investment protects valuable equipment and reduces operational risks in thermally demanding applications.
Sources: https://itsoftwaretips.com/a-simple-guide-to-choosing-the-right-c13-power-cord-for-your-devices/
https://dchatmogul.com/blogs/77824/How-to-Safely-Unplug-a-C13-Cord-A-Complete-Guide