Introduction
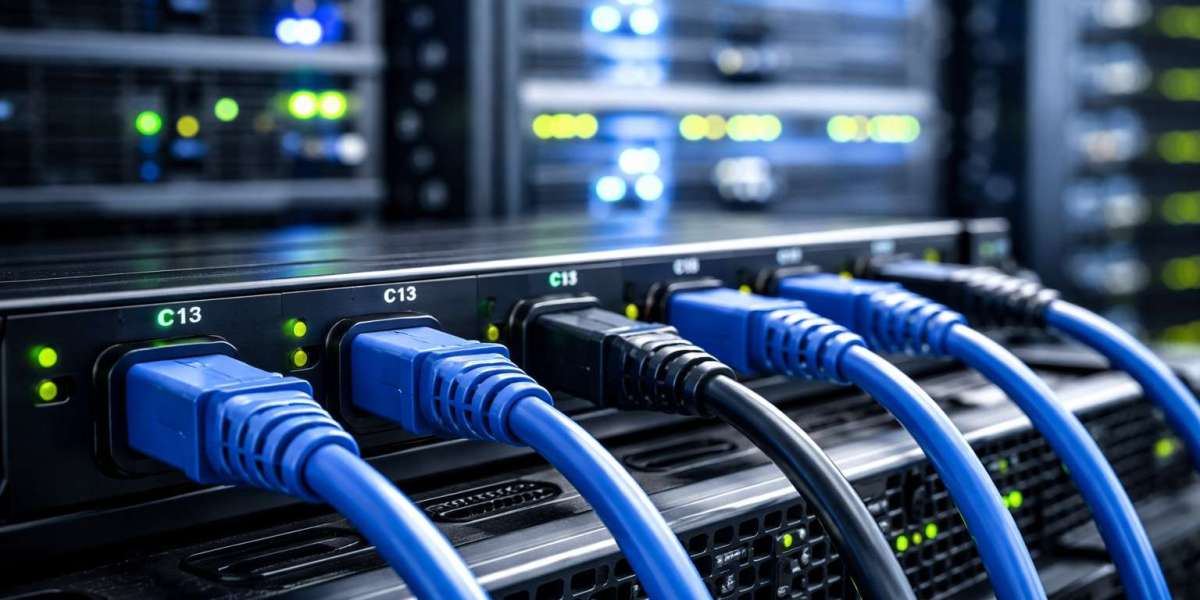
Server racks present one of the most challenging cable management scenarios in any data center. With dozens or even hundreds of devices requiring power, administrators face a tangled web of cables that can impede airflow, complicate maintenance, and create safety hazards. IEC power cords offer a standardized solution that transforms chaotic cable situations into organized, efficient systems. These internationally recognized connectors bring consistency, flexibility, and practicality to server rack environments.
Understanding IEC Power Cords
The International Electrotechnical Commission (IEC) established standardized power connector specifications that manufacturers worldwide now follow. IEC power cords feature universal designs that connect servers, networking equipment, and other rack-mounted devices to power distribution units (PDUs). Unlike proprietary power connections, IEC standards ensure compatibility across different brands and equipment generations, making them the backbone of modern data center infrastructure.
Key Advantages for Cable Management
Standardized Connector Sizes
IEC power cords eliminate the guesswork from cable organization. The standardized connector shapes and sizes allow administrators to plan rack layouts with precision. When you know exactly which types of IEC cables you need, you can order the correct lengths and avoid the excess cable slack that creates clutter. This standardization means replacement cables fit perfectly without requiring adapter searches or custom solutions.
Right-Angle and Locking Options
Many types of IEC cables come with right-angle connectors that point cables parallel to the equipment rather than straight out. This design feature saves valuable rack space and reduces the bend radius required for cable routing. Right-angle connectors keep cables flush against the back of servers, allowing for tighter equipment spacing and improved airflow patterns. Locking IEC connectors add another layer of organization by preventing accidental disconnections during maintenance activities.
Color-Coded Solutions
Cable management improves dramatically when administrators can identify power sources at a glance. Different types of IEC cables come in various colors, enabling teams to create visual mapping systems. Red cables might indicate primary power circuits, while blue cables represent backup power sources. This color-coding system reduces troubleshooting time and prevents accidental disconnections during maintenance work.
Types of IEC Cables for Server Racks
C13 to C14 Cables
The C13/C14 combination represents the most common configuration in server racks. C14 connectors plug into PDUs, while C13 connectors attach to server power supplies. These cables handle up to 10-15 amps, making them suitable for most standard servers and networking equipment. Their universal application across equipment types simplifies inventory management and cable organization strategies.
C19 to C20 Cables
High-power servers and storage arrays require C19/C20 cables, which support higher amperage ratings up to 16-20 amps. These robust connectors feature larger pins and housings, making them visually distinct from standard C13 cables. The size difference helps administrators quickly identify high-power circuits, reducing the risk of overloading standard power connections.
C15 to C16 Cables
Equipment that generates significant heat, such as certain network switches and high-performance computing devices, uses C15/C16 cables. These connectors feature a notched design that prevents accidental connection to standard C13 outlets. The temperature rating of these cables extends to 120°C, providing additional safety margins in hot-running equipment scenarios.
Extension and Jumper Cables
Various types of IEC cables serve specialized purposes within rack environments. Extension cables provide additional reach when PDU placement doesn't align perfectly with equipment locations. Jumper cables with C14 to C13 configurations enable daisy-chaining power between compatible devices, though administrators must carefully monitor amperage loads when using this approach.
Best Practices for Implementation
Cable Length Selection
Proper cable length dramatically improves rack appearance and functionality. Short cables reduce excess slack but may limit flexibility during equipment moves. Standard lengths of 3, 6, and 10 feet cover most server rack scenarios. Administrators should measure actual distances and add 20-30% additional length for routing around cable management arms and through vertical cable managers.
Vertical and Horizontal Management
Strategic placement of vertical cable managers on rack sides creates dedicated pathways for IEC power cords. These channels keep power cables separate from data cables, reducing electromagnetic interference and simplifying troubleshooting. Horizontal cable managers at the rear of equipment maintain organization at connection points. The different types of IEC cables route through these management systems based on their amperage requirements and connection locations.
Labeling Systems
Even with color-coding, comprehensive labeling remains essential. Labels at both ends of IEC power cords identify source PDU outlets and destination equipment. This documentation proves invaluable during emergency troubleshooting or planned maintenance windows. Many organizations implement label schemes that include rack location, circuit information, and equipment identifiers.
Cable Routing Patterns
Consistent routing patterns enhance cable management effectiveness. Many data centers adopt "top-feed" or "bottom-feed" approaches where all power cables enter equipment from the same direction. This consistency creates visual order and makes cable tracing more intuitive. When combining different types of IEC cables in the same rack, administrators group them by amperage rating to simplify circuit calculations.
Safety and Maintenance Benefits
Organized IEC power cord management reduces accident risks in server environments. Technicians can access equipment without navigating through cable obstacles. Clear cable pathways prevent trips and falls during maintenance activities. The standardization of IEC connectors also reduces the risk of connecting equipment to incompatible voltage or amperage sources.
Regular maintenance becomes more manageable with proper IEC cable organization. Administrators can quickly identify which cables connect to which devices, enabling faster equipment swaps and upgrades. When power issues arise, organized cable layouts allow rapid isolation of problematic circuits without affecting nearby equipment.
Conclusion
IEC power cords transform server rack cable management from a persistent challenge into a manageable system. Their standardized designs, variety of configurations, and compatibility across equipment types create organizational possibilities that proprietary connectors cannot match. By selecting appropriate types of IEC cables, implementing consistent routing practices, and maintaining proper documentation, data center administrators create safer, more efficient, and more maintainable server rack environments. The initial investment in quality IEC cables and management infrastructure pays ongoing dividends through reduced troubleshooting time, improved airflow, and enhanced operational reliability.