Firewalls and antivirus software might prevent you from syncing your email and calendar events. After rebuilding the OST file, it’s important to check for any missing mailbox data.
Firewalls and antivirus software might prevent you from syncing your email and calendar events. After rebuilding the OST file, it’s important to check for any missing mailbox data. If you find any missing items in the new OST file, you can recover them from the backup OST file using Stellar Converter for OST. This professional OST to PST converter tool can extract data from the backup OST file and convert it into PST file, which you can easily import into Outloo
To avoid data loss when using cloud applications, perform Office 365 data backup. NAKIVO Backup & Replication is a universal data protection solution that can protect not only Office 365 but also virtual, physical, and cloud environments. Download the software and configure data backup in your environmen
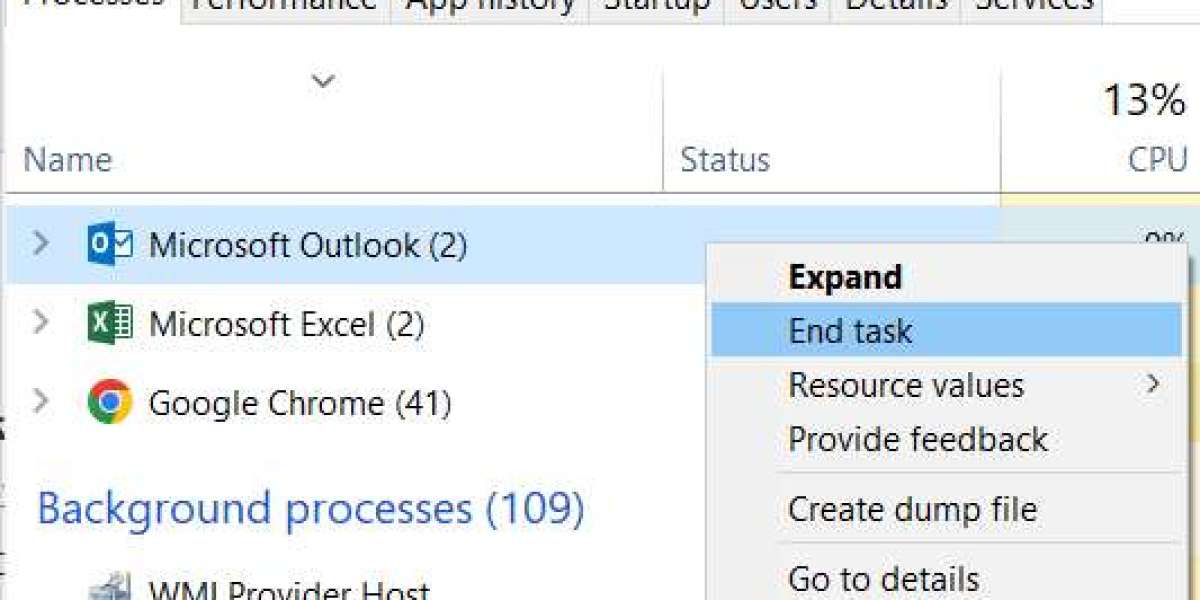
She tests each app and verifies every guide to ensure it’s easy to follow and truly helpful to users. If you lose your connection to the internet, classic Outlook won't be able to send your messages. If you see messages piling up in your Outlook outbox or people you're sending messages to aren't receiving them, try the following methods to fix the issue. Outlook’s rules automate various email tasks,
troubleshoot microsoft account login but sometimes, a rule intended for efficiency might inadvertently divert your messages to an unfamiliar folder. A cluttered cache can impede the smooth functioning of Outloo
An app password is used instead of your normal account password for apps that don't support two-factor authentication. Now, restart Outlook and check if Outlook synchronization is working. While we all use systems differently, I don’t think I have 100GB of data after working for my company almost 25 years, let alone this much email. Online archive can take 24 hours or more to complete, it depends on what you have it set to archive. I think Online Archive may be a harder sell but we need to do it anyway. I’ve turned on Archiving (but no progress as of yet, as expected)…I changed to header and then Download Headers then Full Item
Two-factor authentication helps protect your account by making it more difficult for someone else to sign in. It verifies your identity using your password and a contact method (also known as security info). For a similar error caused by a different issue, refer to Outlook shows Disconnected in status bar if the last character in legacyExchangeDN is a space. To view the scan log, start Outlook, and then open the Deleted Items folder. Any problems are noted in a message that has "OST Integrity Check" as its Subject. The OST Integrity Check Tool (Scanost.exe) is installed when you install Outlook in the following locations, as appropriate for the Outlook version that you are runnin
However, sometimes employees may not have the required permissions to open and edit an item. You can resolve this Office 365 issue simply by purchasing additional cloud storage space from Microsoft. Consider implementing a regular storage cleanup practice with Microsoft 365 recycle bin check
So, comments about his email box size aside (which I cannot change or make him clean up at this time), I need this fixed really fast today. If your password isn't the problem, you might have a certificate error. If so, you'll see a message that says, "There is a problem with the server's security certificate. The security certificate is not from a trusted certifying authority." The Mail and Calendar apps for Windows 10 don't support two-factor authentication. If two-factor authentication troubleshoot microsoft account login is turned on for your account, you'll need to create an app password for that accoun
Performance may be decreased if you use the Outlook AutoArchive feature or sync to Outlook with a mobile device. For more information, see How to install the latest applicable updates for Microsoft Outlook (US English only
From my first day at medical school it took me 10 years to be able to lead an operative team performing a hip replacement. Alongside this I built 3 successful businesses by teaching myself everything from how to code, to how to hire a team to how to develop a winning company culture so that the team was as aligned to the mission as I was. Oh and I'm still learning all of these things in addition to learning guitar, upping my burpee count and practising my Japanese language skills. Luckily this complex physiological mechanism, with a little mental reframing, can actually be your biggest ally in getting started, overcoming fear and moving you outside of your comfort zone to allow you to gro
As your mailbox size increases, more resources are required to open each folder. If you have a large number of items in any single folder, you may experience performance issues during certain operations. For more information, see Outlook performance issues when there are too many items or folders in a cached mode .ost or .pst file. When you install Outlook, an Inbox repair tool (scanpst.exe) is also installed on your PC. The Inbox repair tool can resolve problems by scanning your Outlook data files, and repairing errors. To use the Inbox repair tool, exit Outlook, and then follow the steps in Repair Outlook Data Files (.pst and .ost
 Global Power Steering Fluids Market Industry Insights, Trends, Outlook, Opportunity Analysis Forecast To 2025-2034
Oleh kertina2
Global Power Steering Fluids Market Industry Insights, Trends, Outlook, Opportunity Analysis Forecast To 2025-2034
Oleh kertina2 Repair an Office application
Oleh ashlykime82679
Repair an Office application
Oleh ashlykime82679 Poker Room Online Non AAMS: Analisi delle Dinamiche Competitive e Implicazioni per il Giocatore Italiano
Oleh devidweb
Poker Room Online Non AAMS: Analisi delle Dinamiche Competitive e Implicazioni per il Giocatore Italiano
Oleh devidweb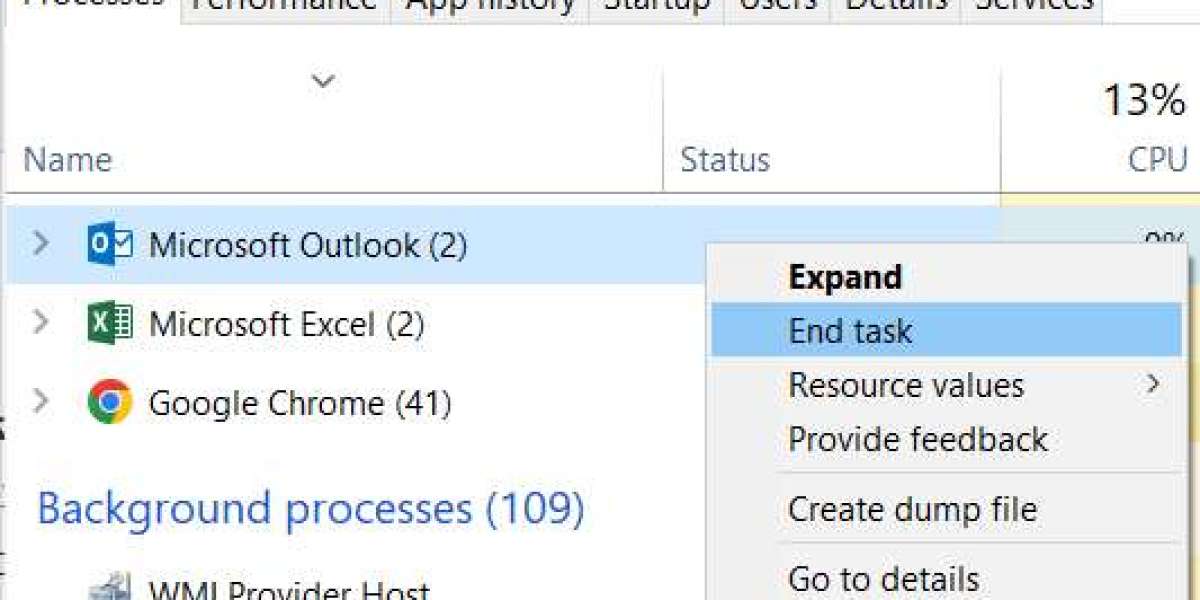 Outlook 2013 2016 stuck on "loading profile" for about 30 seconds Software & Applications
Oleh harrisleong515
Outlook 2013 2016 stuck on "loading profile" for about 30 seconds Software & Applications
Oleh harrisleong515Tree Service Springfield Tips for Safer Trees
Oleh latoshaoliver1